The Effects of Monetary and Fiscal Policies on Environmental Pollutants in Iran: A Nonlinear Approach
Keywords:
monetary policies, financial policies, carbon dioxide, Iran, non-linear approachAbstract
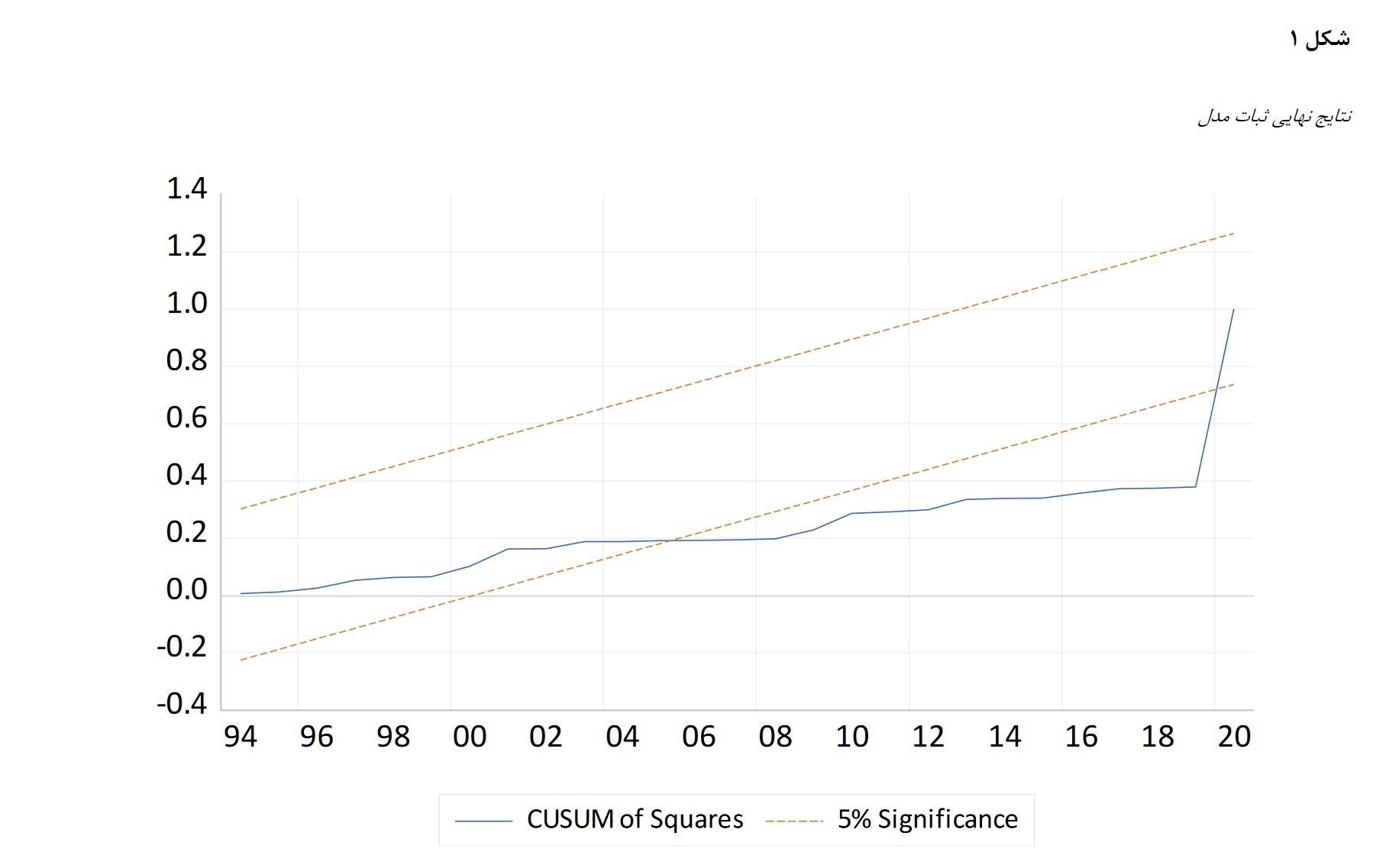
Environmental quality is influenced by various factors, one of the significant factors is monetary and financial policies. Therefore, the present study deals with the effects of monetary and financial policies on environmental pollutants in Iran using a non-linear approach during the years 1980-2020. The results of the study show that in the short term of carbon dioxide emission in the previous period, the economic growth rate, the legal reserve rate and the ratio of taxes to GDP have a positive effect on the emission of environmental pollutants, and government spending has a negative effect on carbon dioxide emission. It has carbon. Non-linear effects of carbon dioxide emissions in the previous period, positive economic growth rate shock, positive economic growth rate shock in the previous period, negative economic growth rate shock in the previous period, positive government expenditure shock, negative government expenditure shock, negative legal reserve rate shock, The positive shock of the ratio of taxes to GDP and the negative shock of the ratio of taxes to GDP had a positive effect on carbon dioxide emissions, and the negative shock of government spending in the previous period and the negative shock of the legal reserve rate had a negative effect on carbon dioxide emissions in the short term. Is. In the long term, the emission of carbon dioxide pollutant in the previous period, the negative shock of the government expenditure in the previous period and the positive shock of the legal reserve rate had a negative effect on the emission of carbon dioxide, and the positive shock of the economic growth rate of the previous period, the negative shock of the economic growth rate, the negative shock of the rate Legal reserves, the positive shock of the ratio of taxes to GDP and the negative shock of the ratio of taxes to GDP have had a positive effect on the emission of carbon dioxide.
Downloads
References
Annicchiarico, B., Di Dio, Fabio. (2017). GHG Emissions Control and Monetary Policy. Environmental and Resource
Economics, 67(4), 823-851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-016-0007-5
Chan, Y. T. (2020). Are macroeconomic policies better in curbing air pollution than environmental policies? A DSGE
approach with carbon-dependent fiscal and monetary policies. Energy Policy, 141, 111454.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111454
Chen, C., Pan, Dongyang. (2020). The optimal mix of monetary and climate policy. Munich Personal RePEc Archive,
no(no), -. https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/97718/
Chishti, M. Z., Ahmad, Manzoor, Rehman, Abdul, Khan, Muhammad Kamran. (2021). Mitigations pathways towards
sustainable development: Assessing the influence of fiscal and monetary policies on carbon emissions in BRICS
economies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 292, 126035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126035
Dongyan, L. (2009). Fiscal and tax policy support for energy efficiency retrofit for existing residential buildings in
China's northern heating region. Energy Policy, 37(6), 2113-2118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.11.036
Emadi, S. J., Elahi, Naser, Komijani, Akbar, Kiyaalhoseini, Seyed Ziyaaodin. (2019). Investigate effect of interaction
monetary and fiscal policies on economic growth in Iran. The Journal of Economic Studies and Policies, 6(2), 3-28.
https://economic.mofidu.ac.ir/article_37180_f0dba76139498481e6f0a62331d82b03.pdf
Hajdukovic, I. (2021). Interactions among macroeconomic policies, the energy market and environmental quality.
Environmental Economics and Policy Studies, 23(4), 861-913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10018-021-00305-x
Halkos, G. E., & Paizanos, E. Α. (2016). The effects of fiscal policy on CO2 emissions: Evidence from the U.S.A. Energy
Policy, 88(no), 317-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.10.035
Halkos, G. E., Paizanos, Epameinondas Α. (2013). The effect of government expenditure on the environment:An
empirical investigation. Ecological Economics, 91(no), 48-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.04.002
Hosseini, E., Nademi, Younes, Asayesh, Hamid, Sajadifar, Seyed Hossein. (2021). The Interactions of Instability of
Monetary and Fiscal Policies in the Iranian Economy by the MSVAR Approach. Journal of Applied Economics
Studies in Iran, 10(37), 169-199. https://doi.org/10.22084/aes.2020.22565.3156
Komijani, A., Kavand, Hossein, Abbasinejad, Hossein. (2010). Lack of Independency in Monetary Policy and the Role
of Oil Price in Monetary and Fiscal Policy: The Case of Iran. The Journal of Economic Studies and Policies, no(17),
-32. https://economic.mofidu.ac.ir/?_action=export&rf=enw&rc=47826&lang=en
Liu, Y., Han, Liyan, Yin, Ziqiao, Luo, Kongyi. (2017). A competitive carbon emissions scheme with hybrid fiscal
incentives: The evidence from a taxi industry. Energy Policy, 102, 414-422.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.12.038
López, R., Galinato, Gregmar I, Islam, Asif. (2011). Fiscal spending and the environment: Theory and empirics. Journal
of Environmental Economics and Management, 62(2), 180-198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2011.03.001
Mahdavi, A., Amirbabaei, Sonay. (2016). The Effects of Financial Development on the Quality of Environment in Iran
(1973 - 2007). The Economic Research (Sustainable Growth and Development), 15(4), 1-23.
http://ecor.modares.ac.ir/article-18-4160-en.html
Matikainen, S., Campiglio, Emanuele, Zenghelis, Dimitri. (2017). The climate impact of quantitative easing. Policy
Paper, Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment, London School of Economics and
Political Science, 36(no), 1-36. https://www.lse.ac.uk/granthaminstitute/wpcontent/uploads/2017/05/ClimateImpactQuantEasing_Matikainen-et-al.pdf
McAusland, C. (2008). Trade, politics, and the environment: Tailpipe vs. smokestack. Journal of Environmental
Economics and Management, 55(1), 52-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2007.08.002
McKibbin, W. J., Morris, A. C., Panton, A., & Wilcoxen, P. (2017). Climate change and monetary policy: Dealing with
disruption. CAMA Working, no(no), 77. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3084399
Noureen, S., Iqbal, Javed, Chishti, Muhammad Zubair. (2022). Exploring the dynamic effects of shocks in monetary and
fiscal policies on the environment of developing economies: evidence from the CS-ARDL approach. Environmental
Science and Pollution Research, 29(30), 45665-45682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19095-0
Qingquan, J., Khattak, Shoukat Iqbal, Ahmad, Manzoor, Ping, Lin. (2020). A new approach to environmental
sustainability: Assessing the impact of monetary policy on CO2 emissions in Asian economies. Sustainable
Development, 28(5), 1331-1346. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2087
Rausch, S. (2013). Fiscal consolidation and climate policy: An overlapping generations perspective. Energy Economics,
(no), S134-S148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2013.09.009
Shin, Y., Yu, Byungchul, Greenwood-Nimmo, Matthew. (2014). Modelling Asymmetric Cointegration and Dynamic
Multipliers in a Nonlinear ARDL Framework. In R. C. Sickles & W. C. Horrace (Eds.), Festschrift in Honor of Peter
Schmidt: Econometric Methods and Applications (pp. 281-314). Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-
-8008-3_9
Ullah, S., Majeed, Muhammad Tariq, Chishti, Muhammad Zubair. (2020). Examining the asymmetric effects of fiscal
policy instruments on environmental quality in Asian economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,
(30), 38287-38299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09859-x
Yuelan, P., Akbar, Muhammad Waqas, Hafeez, Muhammad, Ahmad, Manzoor, Zia, Zeenat, Ullah, Sana. (2019). The
nexus of fiscal policy instruments and environmental degradation in China. Environmental Science and Pollution
Research, 26(28), 28919-28932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06071-4
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










