A Model for Operational Budgeting in Fossil Fuel Power Plants Based on Machine Learning and Grounded Theory
Keywords:
operational budgeting, power plants, fossil fuels, machine learning, electricity productionAbstract
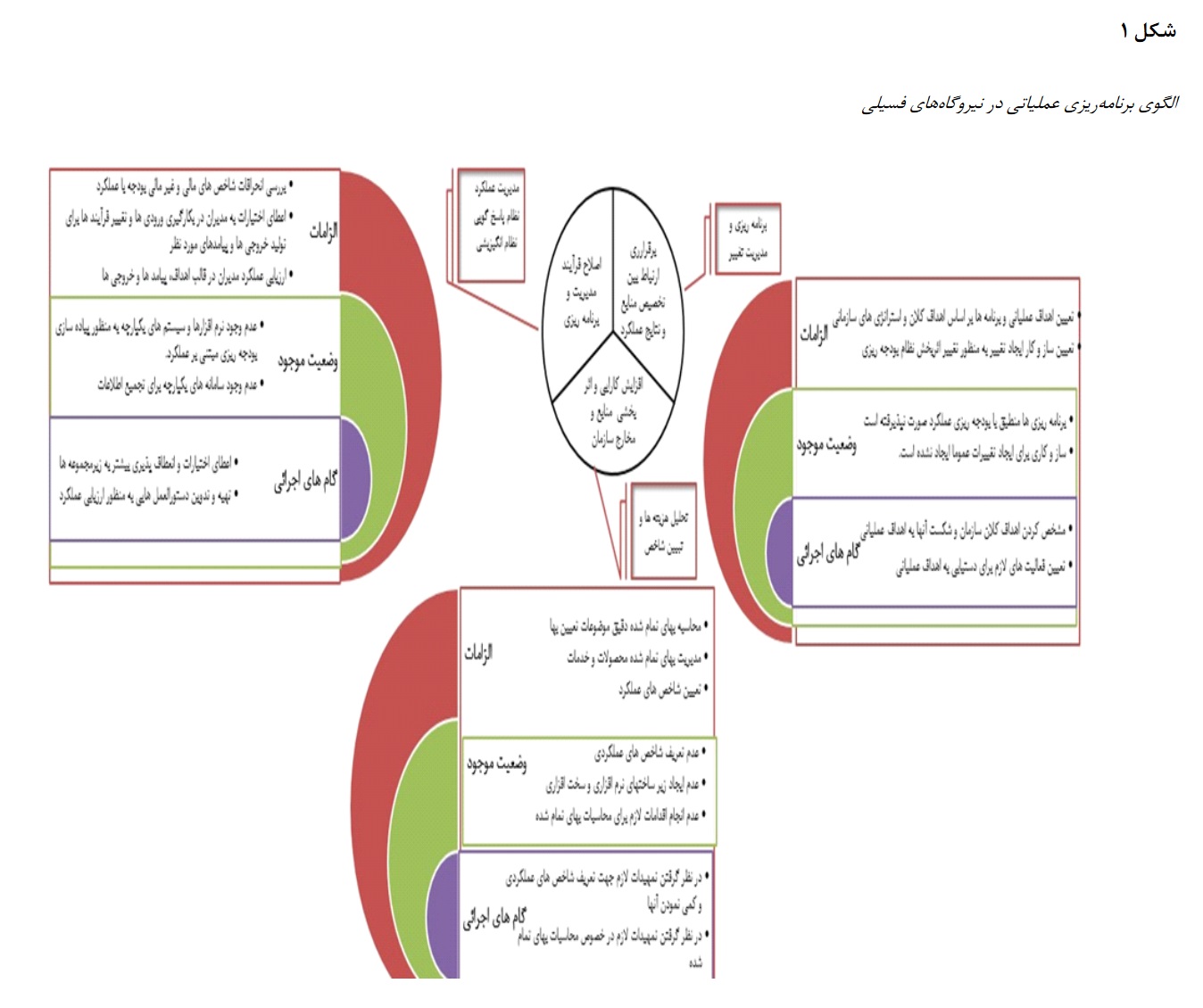
The present study aims to provide a comprehensive model for operational budgeting in fossil fuel power plants based on machine learning and grounded theory. This research examines the impact of a participatory approach to performance-based budgeting on accountability in the public sector. Performance-based budgeting establishes a foundation for greater accountability in the utilization of organizational resources. Additionally, issues such as environmental protection, the high cost of initial investment, and optimal resource utilization play a direct role in the performance of market participants. Unfortunately, in the new competitive conditions, traditional and classical models that assume economic agents (producers or consumers) are homogeneous and lack interaction do not provide the necessary efficiency or satisfactory results. Operational analysis elucidates the behavior of heterogeneous production units and allows for interaction and learning in a dynamic environment. However, due to the model's vast scope and complexities, an analytical solution cannot be used to obtain variables under equilibrium conditions. Considering advances in computational technology, the results of agent-based models can typically be evaluated using simulation methods within various scenarios. Production units submit their proposed production schedules for each hour to the operating entity daily. This entity, based on the forecasted demand for the next twenty-four hours and by implementing an auction mechanism, determines the winning units and market price, followed by executing a settlement mechanism for sales and payments. Given the necessity of balancing consumption and production across the country and the geographical distribution of production and consumer units, the auction mechanism considers not only the consumption amount but also the economic and technical constraints related to production, transmission, and distribution. The research findings indicate that existing performance-based budgeting infrastructures have no effect on financial accountability in the public sector, whereas they have a negative impact on operational accountability. Implementing performance-based budgeting infrastructures and adopting a participatory approach in budgeting enhances the level of governmental accountability in the public sector.
Downloads
References
Babaei, M., Fattahi Masrour, F., & Shakeri, N. (2020). Qualitative Sports Development Model for All in Iran by
Grounded Theory. Strategic Studies on Youth and Sports, 19(49), 95-112.
https://faslname.msy.gov.ir/article_393.html
Chen, J., Wen, Y., Nanehkaran, Y. A., Suzauddola, M. D., Chen, W., & Zhang, D. (2023). Machine learning techniques
for stock price prediction and graphic signal recognition. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 121,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106038
Daneshfard, K., & Shiravand, S. (2012). Barriers of operational treatment budget in Islamic Republic of Iran, ministry of
health and medical education. J-Gorgan-Univ-Med-Sci, 14(2), 90-96. http://goums.ac.ir/journal/article-1-1328-
en.html
García-Martín, E., Rodrigues, C. F., Riley, G., & Grahn, H. (2019). Estimation of energy consumption in machine
learning. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 134, 75-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2019.07.007
Golabchi, H., Kiaee, M., & Kameli, M. J. (2024). Designing a Superior Service Delivery Model in Education to Enhance
Public Satisfaction [Research Article]. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology, 7(1), 189-197.
https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.ijes.7.1.18
Heo, B.-Y., Kim, M. J., & Heo, W.-H. (2020). An algorithm for validation of the efficiency of disaster and safety
management budget investment in South Korea. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 47, 101566.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101566
Heydari Rad, P., Hamidi, M., Sajjadi, S. N., & Rajabi Noushabadi, H. (2023). Providing a Framework of Analyzing the
Effective Factors on the Success of Small Businesses of Sports Service [Research Article]. Iranian Journal of
Educational Sociology, 6(2), 97-111. https://doi.org/10.61186/ijes.6.2.97
Jahanbini, E., Pifeh, A., & Dehghanzadeh, H. (2022). Investigating the Impact of Budgeting Methods on Optimal
Resource Allocation. Accounting and Auditing Studies, 11(44), 69-90. https://doi.org/10.22034/iaas.2022.168256
Kumar, N., & Aeron, P. K. G. A. (2024). Beyond Automation: Exploring the Synergy of Cloud, AI, Machine Learning,
and IoT for Intelligent Systems. Jes, 20(3s), 1356-1364. https://doi.org/10.52783/jes.1511
Makala, B., & Bakovic, T. (2020). Artificial intelligence in the power sector. International Finance Corporation:
Washington, DC, USA. https://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/239631596432312564/pdf/ArtificialIntelligence-in-the-Power-Sector.pdf
Miri Rami, S. F., Delgoshaei, Y., & Mahmoudi, A. H. (2022). Identification and Analysis of Effective Factors on the
Strategic Intelligence of Education Districts Managers of Tehran City and Provide an Appropriate Model [Research
Article]. Iranian Journal of Educational Sociology, 5(1), 113-125. https://doi.org/10.61186/ijes.5.1.113
Muthomi, F., & Thurmaier, K. (2021). Participatory Transparency in Kenya: Toward an Engaged Budgeting Model of
Local Governance. Public Administration Review, 81(3), 519-531. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13294
Namazi, M., Nazemi, A., Namazi, N. R., & Moazzeni, E. (2023). Investigating Performance-based Budgeting and
Performance Control in Iran's Executive Apparatus Using Balanced Scorecard Technique. Empirical Studies in
Financial Accounting, 20(77), 37-72. https://doi.org/10.22054/qjma.2023.69417.2400
Namazi, M., & Rezaei, G. (2023). Modelling the role of strategic planning, strategic management accounting information
system, and psychological factors on the budgetary slack. Accounting Forum, 1-28.
https://doi.org/10.1080/01559982.2022.2163040
Sadeghi, H., Amin Mousavi, S. A., & Rah Chamni, A. (2023). Designing of a Framework for Applying Business
Intelligence to Improve the Relationship between Academia and Industry. Journal of value creating in Business
Management, 2(4), 106-129. https://doi.org/10.22034/jvcbm.2023.389647.1077
Setyani, S., Hanifah, I. A., & Ismawati, I. (2022). The Role of Budget Decision Making as a Mediation of Accounting
Information Systems and Organizational Culture on the Performance of Government Agencies. Journal of Applied
Business Taxation and Economics Research. https://doi.org/10.54408/jabter.v1i3.59
Yahya, Y., & Rukun, K. (2016). Leadership in Planning and Budgeting on Higher Education.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 1403 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










