Explanation of the Dynamic Model of the Medicinal Plants Industry Entrepreneurship Ecosystem
Keywords:
Entrepreneurship, Entrepreneurial ecosystem, Medicinal plants, System dynamicsAbstract
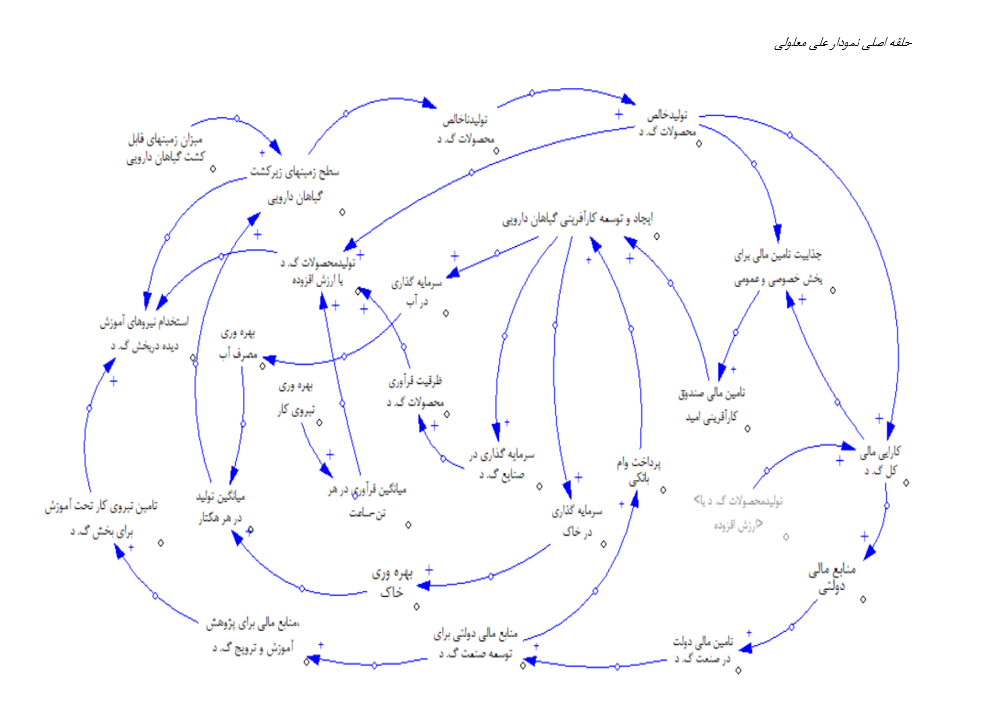
This study aims to explain the dynamic model of the entrepreneurial ecosystem in the medicinal plants industry to enhance the understanding of the complexities and dynamics of this sector, identify existing entrepreneurial opportunities, create jobs, and improve the productivity of production factors, including arable land, water resources, and human capital. This research is applied-developmental in terms of its objective and exploratory in terms of the data collection method, using a mixed (quantitative and qualitative) approach. Initially, related variables were identified through a review of the literature. Subsequently, the relationships between the variables were extracted through an examination of prior research. In the next stage, semi-structured interviews with experts were conducted to complete the relationships between the variables in the model. Finally, based on system dynamics, a causal-loop diagram of this ecosystem was developed. The study's population consists of entrepreneurs in the medicinal plants industry within the entrepreneurial ecosystem framework. In the findings from the explanation of the causal model of the study, five subsystems of the entrepreneurial ecosystem were identified. The first subsystem focuses on medicinal plant production and development, which also examines the country's population. The second subsystem pertains to financing and investment in medicinal plant development, which considers their responsiveness to other variables, such as the exchange rate. The third subsystem addresses entrepreneurial ecosystem development, including supportive policies, entrepreneurial opportunities, and marketing. The fourth subsystem deals with the productivity of production factors, involving water resources, land, and human labor. The fifth subsystem, the cultural factors subsystem, addresses the cultural aspect and was added to the model to address the research gap that existed in this field. Then, the key variables in each subsystem and their causal relationships within the subsystems, as well as the interrelationships between the subsystems, were modeled in the form of a causal-loop diagram. Another gap addressed by this research is the investigation of the entrepreneurial ecosystem of medicinal plants, which has not been studied using system dynamics before. Additionally, presenting a new classification of subsystems is an innovation in this study. All five identified categories of factors have complex interrelations, typically of a direct nature. By establishing appropriate connections between the variables of this ecosystem, not only is an improvement in the productivity of production factors (including arable land, water resources, and human capital) achieved, but individual benefits for entrepreneurs and social benefits for the community are also realized.
Downloads
References
Audretsch, D. B., Cunningham, J. A., Kuratko, D. F., Lehmann, E. E., & Menter, M. (2019). Entrepreneurial ecosystems:
economic, technological, and societal impacts. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 44(2), 313-325.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9953-8
Bouncken, R. B., & Kraus, S. (2022). Entrepreneurial ecosystems in an interconnected world: emergence, governance and
digitalization. Review of managerial science, 16, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-021-00444-1
Corrente, S., Greco, S., Nicotra, M., Romano, M., & Schillaci, C. E. (2019). Evaluating and comparing entrepreneurial
ecosystems using SMAA and SMAA-S. The Journal of Technology Transfer, 44(2), 485-519.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-018-9684-2
Davari, A., Sefidbari, L., & Baghersad, V. (2017). The Factors of Iran's Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Based on the Isenberg
Model. Entrepreneurship Development, 10(1), 101-120. https://jed.ut.ac.ir/article_62306_en.html
Dias, C. S. L., Rodrigues, R. G., & Ferreira, J. J. (2019). What's new in the research on agricultural entrepreneurship? Journal
of Rural Studies, 65, 99-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2018.11.003
Ganjhu, R. K., Mudgal, P. P., & Maity, H. (2015). Herbal plants and plant preparations as remedial approach for viral diseases.
Virusdisease, 26, 225-236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-015-0276-6
Hosseinzadeh, M., Samadi Foroushani, M., & Sadraei, R. (2022). Dynamic performance development of entrepreneurial
ecosystem in the agricultural sector. British Food Journal, 124(7), 2361-2395. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-08-2021-0909
Isenberg, D. (2011). The entrepreneurship ecosystem strategy as a new paradigm for economic policy: Principles for cultivating
entrepreneurship. Presentation at the Institute of International & European Affairs,
Jafari-Sadeghi, V., Kimiagari, S., & Biancone, P. P. (2019). Level of education and knowledge, foresight competency and
international entrepreneurship: a study of human capital determinants in the European countries. European Business
Review, 32(1), 46-68. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-05-2018-0098
Jha, S. K. (2018). Entrepreneurial ecosystem in India: taking stock and looking ahead. IIMB Management Review, 30(2), 179-
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iimb.2018.04.002
Keim, J. (2024). Depolarizing innovation: Dynamic policy implications for entrepreneurial ecosystems in second-tier European
regions. Junior Management Science (JUMS), 9(1), 1211-1240.
https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/290633/1/1884465242.pdf
Kirillova, O. V., Amirova, E. F., Kuznetsov, M. G., Valeeva, G. A., & Zakharova, G. P. (2020). Innovative directions of
agricultural development aimed at ensuring food security in Russia. Bio Web of Conferences, 17, 00068.
https://doi.org/10.1051/bioconf/20201700068
Kosasih, K. (2024). The Social Entrepreneurship Approach to Improve the Medicinal Efficient Wild Plants' Economic Value
in the Community. IJEBMR. https://doi.org/10.51505/IJEBMR.2024.8702
Martínez-Fierro, S., Biedma-Ferrer, J. M., & Ruiz-Navarro, J. (2020). Impact of high-growth start-ups on entrepreneurial
environment based on the level of national economic development. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(3), 1007-
https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2413
Mason, C. (2019). Entrepreneurial ecosystems: emerging research questions. Presentation to the 2019 ACERE Conference,
University of Technology, Sydney.
Motamedi Nia, Z., Movahed Mohammadi, S. H., Alambeygi, A., & Mahdizadeh, H. (2024). Elements of the Isenberg
Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Model in the Context of Agricultural Higher Education. Iranian Journal of Agricultural
Economics and Development Research, 55(1). https://ijaedr.ut.ac.ir/article_81833.html?lang=en
Noorhosseini, A., Fallahi, E., Allahyari, M. S., Qolizadeh, S., & Majlesi, S. (2017). Identifying Economic, Educational, and
Extension Activities Impacting the Development of Medicinal Plant Cultivation Areas: Comparing Entropy Weighting
and Triangular Fuzzy Delphi Methods. Agricultural Education and Extension Research Quarterly, 10(4), 1-12.
http://journals.srbiau.ac.ir/article_11672.html
Okereke, S. C., Ijeh, I. I., & Arunsi, U. O. (2017). Determination of bioactive constituents of Rauwolfia vomitoria Afzel
(Asofeyeje) roots using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and Fourier transform infrared spectrometry
(FT-IR). African J Pharm Pharmacol, 11, 25-31. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP2016.4712
Pariasa, I. I., & Hardana, A. E. (2024). The Impact of Farm Production Factors on The Income of Horticultural Farmers in East
Java. HABITAT, 35(1), 19-30. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.habitat.2024.035.1.3
Rao, B. R., Batni, A. R., & Shrivastava, P. (2024). Fostering Agriculture Ecosystem for Sustainability. In Digital Agricultural
Ecosystem: Revolutionary Advancements in Agriculture (pp. 211-228). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781394242962.ch12
Rathore, R. (2022). Entrepreneurial behavior of farmers towards cultivation of medicinal and aromatic plants in the Ujjain
district of Madhya Pradesh. Indian Research Journal of Extension Education, 22(4), 64-67.
https://doi.org/10.54986/irjee/2022/oct_dec/64-67
Reyisi, A., Shiehki Tash, M., Salarzehi, H., & Vali Nafs, A. (2016). Identifying and Prioritizing Factors Influencing
Agricultural Entrepreneurship Development in Rural Areas (Case Study: Sarbaz County).
Shwetzer, C., Maritz, A., & Nguyen, Q. (2019). Entrepreneurial ecosystems: a holistic and dynamic approach. Journal of
Industry-University Collaboration, 1(2), 79-95. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIUC-03-2019-0007
Stam, E., & Van de Ven, A. (2021). Entrepreneurial ecosystem elements. Small Business Economics, 56, 809-832.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-019-00270-6
Stam, F. C., & Spigel, B. (2016). Entrepreneurial ecosystems. USE Discussion paper series, 16(13).
https://ideas.repec.org/p/use/tkiwps/1613.html
Sterman, J. (2000). Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. Irwin/McGraw-Hill.
plex_World
Tang, O., & Rehme, J. (2017). An investigation of renewable certificates policy in Swedish electricity industry using an
integrated system dynamics model. International Journal of Production Economics, 194, 200-213.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.03.012
Urgessa, O. (2024). Effects of real effective exchange rate volatility on export earnings in Ethiopia: symmetric and asymmetric
effect analysis. Heliyon, 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23529
Worku, M. (2023). Production, productivity, quality and chemical composition of Ethiopian coffee. Cogent Food Agric, 9.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










