Presentation of an Antifragility Model in Iranian Financial Organizations through Thematic Analysis
Keywords:
Antifragility, financial organizations, Thematic AnalysisAbstract
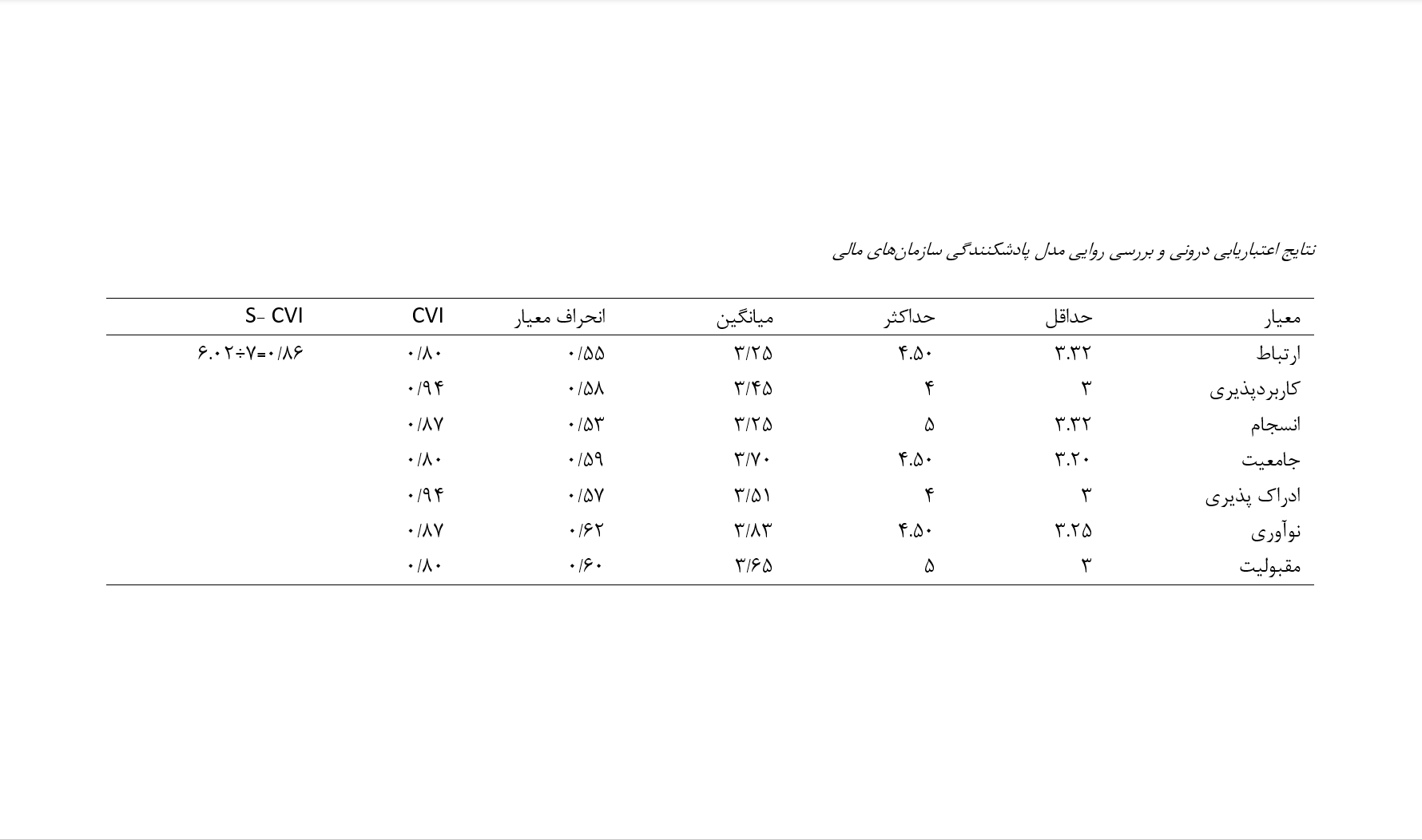
The present study aims to propose a qualitative antifragility model for Iranian financial organizations. The research methodology, in terms of data collection and execution, is qualitative. To design the model, thematic analysis was employed. Subsequently, the validity of the model's dimensions was determined using content validity indices (CVI, CVR, and S-CVI). The statistical population of the study consists of managers of financial organizations and university professors in Iran. The theoretical saturation was reached after conducting interviews with 10 experts in the field related to the research topic. The research findings led to the identification of 79 codes and 19 themes, categorized into four main groups: (1) Random and Environmental Category, which includes components such as flexibility, financial crisis, resilient performance, agility, and adaptability; (2) Financial Performance Category, including components like cost control, financial performance of institutions, central bank independence, inflation volatility, and cash flow management; (3) Managerial Category, comprising components such as risk management, economic growth improvement, capital management, financial policies, and government relations; and (4) Organizational Category, including components such as innovation and creativity, adaptability, resistance and confrontation, integration, and service empowerment. Additionally, the model's validity results indicate that it possesses a high level of content validity.
Downloads
References
Babovic, F., Babovic, V., & Mijic, A. (2018). Antifragility and the development of urban water infrastructure.
International journal of water resources development, 34(4), 499-509.
https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2017.1369866
Bayat, M., & Khansari, M. (2021). Resilience of Random Boolean Networks Using Network Entropy. First National
Conference on Complex Systems with a Focus on Network Science, Tehran.
Blečić, I., & Cecchini, A. (2017). On the antifragility of cities and of their buildings. City, Territory and Architecture, 4,
-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40410-017-0062-4
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational research: Planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative
research. Sage publications. https://repository.unmas.ac.id/medias/journal/EBK-00121.pdf
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2005). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches.
Sage publications. https://www.ucg.ac.me/skladiste/blog_609332/objava_105202/fajlovi/Creswell.pdf
Danchin, A., Binder, P. M., & Noria, S. (2015). Antifragility and tinkering in biology (and in business) flexibility provides
an efficient epigenetic way to manage risk. Genes, 2(4), 998-1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes2040998
Größler, A. (2020). A managerial operationalization of antifragility and its consequences in supply chains. Systems
Research and Behavioral Science, 37(6), 896-905. https://doi.org/10.1002/sres.2759
Iqbal, N. (2016). Analysis of the Educational System from the Resilience Perspective. Electricity Era Journal, 3(5), Fall.
https://noavaryedu.oerp.ir/journal/editorial.board
Mohammadi, T., Shakeri, A., Taghavi, M., & Ahmadi, M. (2017). Elucidating the Concept, Dimensions, and Components
of Economic Resilience. Strategic Studies Journal of Basij, 20(75). https://www.bsrq.ir/article_80461.html?lang=fa
Momeni, S. M., Qasemi, A. R., Shahbazi, M., & Safari, A. (2021). Analysis of Resilience in the Service Supply Chain
in the Iranian Insurance Industry. Future Management Journal(67), 183-198.
https://www.sid.ir/fa/journal/SearchPaperlight.aspx?str=%D8%B2%D9%86%D8%AC%DB%8C%D8%B1%D9%
%20%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%85%DB%8C%D9%86%20%D8%AE%D8%AF%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%AA
Munoz, A., Billsberry, J., & Ambrosini, V. (2022). Resilience, robustness, and antifragility: Towards an appreciation of
distinct organizational responses to adversity. International Journal of Management Reviews, 24(2), 181-187.
https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12289
Qasemi, H. A. M., & Abbas. (2019). Estimating the Resilience Index of the Monetary and Financial Sector of the Iranian
Economy. Applied Economic Theories Journal, 6(3). https://www.sid.ir/paper/386094/fa
Rahimian Asal, M. M., & Maleki, M. H. (2023). A Model for Evaluating Supply Chain Resilience: A Case Study of
Daroupakhsh Distribution Company. Decision Making and Operations Research Journal, 8(1). https://www.journaldmor.ir/article_188158.html
Ramezani, J., & Camarinha-Matos, L. M. (2019). A collaborative approach to resilient and antifragile business
ecosystems.
Saidi Ravani, N., Mahdinejad, H., & Bayat, M. (2018). Spatial Distribution of Housing Poverty and Access to Welfare
Facilities in Shahriar City. International Conference on Security, Progress, and Sustainable Development of Border
Areas, Territorial Regions, and Metropolises: Solutions and Challenges with a Focus on Passive Defense and Crisis
Management, Tehran.
Taleb, N. N. (2012). Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder (Translated by Mina Safari, Edited by Behnam Fallah
ed.). Novin Tose'e Publications. http://kgt.bme.hu/files/BMEGT30M400/Taleb_Antifragile__2012.pdf
Taleb, N. N. (2013). 'Antifragility' as a mathematical idea. Nature, 494(7438), 430-430. https://doi.org/10.1038/494430e
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










